 TOP
TOPChapter 9 Design of the hydraulic circuit's local circuit and application circuit
9-1 direction control circuit (DIRECTION CONTROL CIRCUIT)
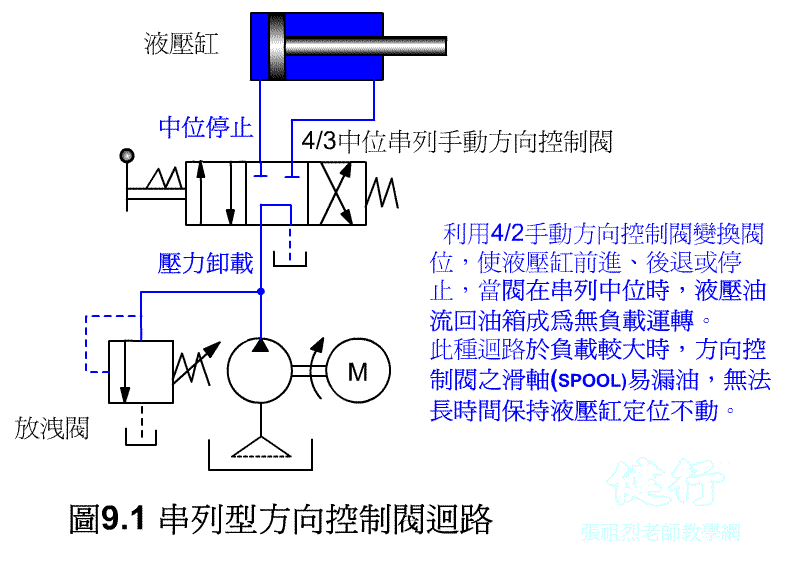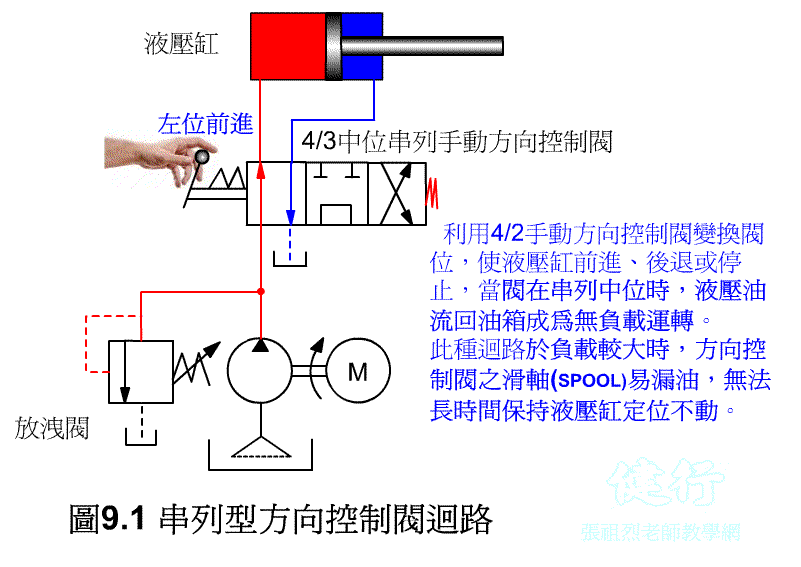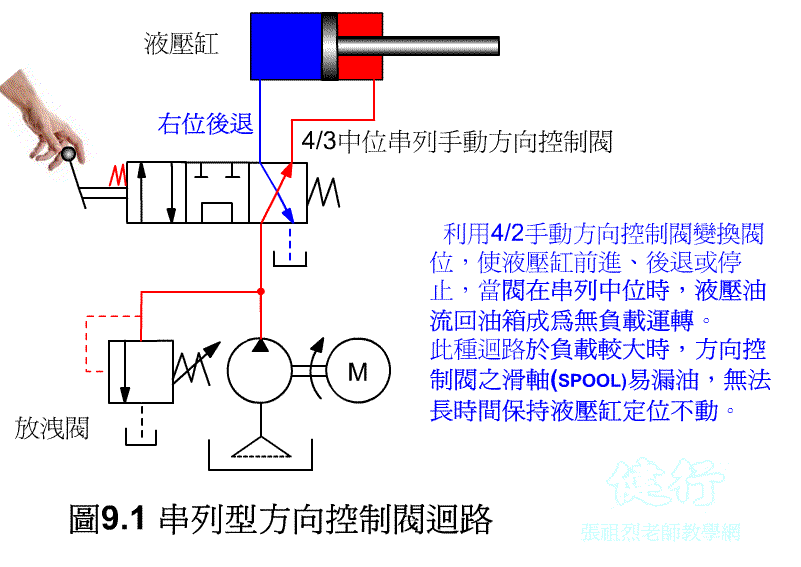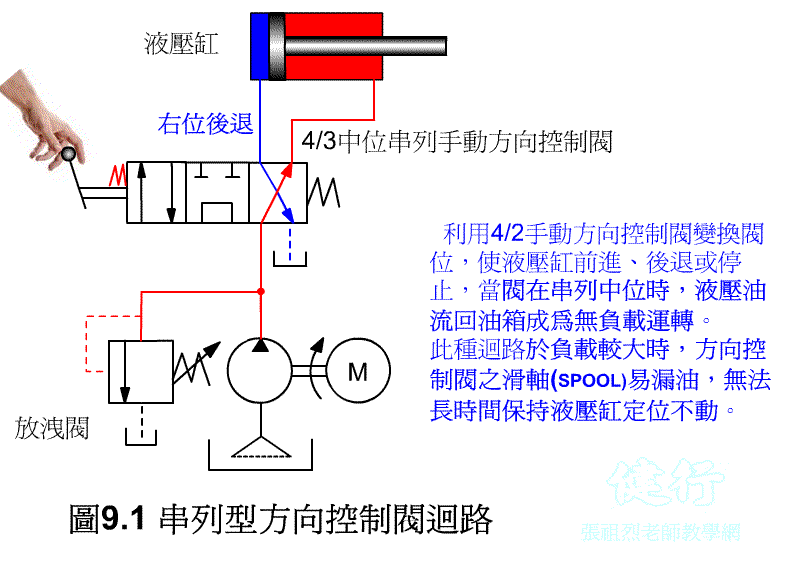
Tandem directional control valve circuit
Pilot check valve locking circuit
Pneumatic guidance control loop
9-2 pressure control loop (PRESSURE CONTROL CIRCUIT)
Pressure setting circuit (PRESSURE CONTROL Circuit)
No load circuit (Unloading Circuit)
Decompression circuit (Reducing Circuit)
Booster circuit (Booster Circuit)
Loop sequence (Sequence Circuit)
Counter circuit (Counterbalance Circuit)
Accumulator circuits (Accumulator Circuit)
9-3 Speed Control Loop (FLOW CONTROL CIRCUIT)
The amount of the (Meter-in) loop
Deceleration circuit (Deceleration Circuit)
Differential circuit (Differential Circuit)
Hydraulic oil supplement circuit (Prefill Circuit)
Synchronization circuit (Synchronizing Circuit)
Pneumatic and hydraulic combined circuit
9-4 Hydraulic motor control circuit
Hydraulic motor counterbalance circuit
9-5 Electric - hydraulic control circuit
Electrical-directional control loop
Two-stage transmission circuit
Synchronous circuit of hydraulic cylinders connected in parallel
Synchronous circuit of hydraulic cylinders connected in series
9-6 Design Principles of Hydraulic Circuit
Goto Zulie teacher teaching network gas hydraulic control practice
3. Moderately increase the system pressure and reduce the volume occupied by the system
4. Fully understand the hydraulic load condition, movement speed, action sequence, friction coefficient and surrounding working environment and other factors.
5. Use standard hydraulic components as much as possible, easy to replace in case of failure.
6. Try to avoid the vibration, noise and heat generated by the hydraulic equipment to improve efficiency.
7. Ensure the safety and reliability of the system circuit . When an emergency occurs, it can be stopped urgently, and if necessary, the hydraulic cylinder can be instantly backed back.
8. When designing, it is necessary to consider the operation, management and maintenance issues . In case of failure, is it convenient to disassemble, disassemble and adjust.
=======================================
9-1 direction control circuit (DIRECTION CONTROL CIRCUIT) P495 the TOP
9-1-1 tandem directional control valve circuit P496
9-1-2 pilot check valve locking circuit P496 TOP
9-1-3 Air pressure guidance control loop P496 TOP
9-2 壓力控制迴路 (PRESSURE CONTROL CIRCUIT) P497 TOP
(一) 放洩閥壓力設定迴路 P498
(二) 高低兩壓力放洩閥迴路 P498 TOP
(三) 平衡活塞放洩閥之通氣孔 (Vent port) 之利用 P499 TOP
(四) 遙控高、中、低壓放洩閥迴路 P499 TOP
9-2-2 無負載迴路 (Unloading Circuit) P500 TOP
(二) 中位旁通無負載迴路 P501 TOP
( 3 ) Hydraulic guidance operation without load circuit P501 TOP
( 4 ) Electromagnetic operation without load circuit P501 TOP
( 5 ) No load circuit of high and low pressure pump P502 TOP
( 6 ) P503 TOP of oil circuit using unloading valve
( 7 ) Variable displacement pump no load circuit P503 TOP
9-2-3 decompression circuit (Reducing Circuit) P504 TOP
( 1 ) Decompression circuit (1)
( 2 ) Pressure reducing circuit (2) TOP
( 3 ) Pressure reducing circuit (3) P505 TOP
( 4 ) Pressure reducing circuit (4) P506 TOP
9-2-4 booster circuit (Booster Circuit) P506 TOP
( 2 ) Booster circuit (2) P507 TOP
( 3 ) Booster circuit (3) P507 TOP
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------
9-2-5 sequence circuit (Sequence Circuit) P508 TOP
( 1 ) Sequence circuit of double cylinder double sequence valve
The set pressure of the sequence valve should be greater than the operating pressure of the hydraulic cylinder and should be less than the system pressure
( 2 ) Sequence circuit P509 TOP of double cylinder single sequence valve
( 3 ) Independent action sequence valve circuit P509 TOP
( 4 ) High-pressure and low-pressure hydraulic pump sequence circuit P51 1 TOP
( 5 ) Cam operation direction control valve sequence circuit P51 1 TOP
( 6 ) Hydraulic guide sequence circuit P512 TOP
( 7 ) Electrical control sequence circuit P512 TOP
( 8 ) Sequence circuit of pressure switch and solenoid valve 4 TOP
9-2-6 contend circuit (counterbalance Circuit) P514 TOP
Hydraulic cylinder counterbalance circuit P515
9-2-7 accumulator circuit (Accumulator Circuit) P515 the TOP
( 1 ) Pressure buffer circuit
( 2 ) Pressure maintaining circuit TOP
( 3 ) Shorten the working cycle time loop TOP
9-3 speed control loop (the FLOW CONTROL CIRCUIT) P519 the TOP
9-3-1 amount of the (Meter-in) loop
The flow control valve is placed on the inlet side of the hydraulic cylinder to adjust the flow to the hydraulic cylinder to control the movement speed of the hydraulic cylinder. The remaining hydraulic oil flows back to the oil tank through the drain valve. The measuring circuit is used in the case of positive load with small load inertia. In this circuit, since the sliding shaft of the directional control valve will have hydraulic oil leakage, the flow control is not correct. Efficiency is generally not high at around 30% .
9-3-2 Measure (Meter-out) circuit
P519 the
TOP
system the flow control valve disposed at the outlet side of the hydraulic
cylinder to control the amount of hydraulic oil flowing out of the hydraulic
cylinder, the excess hydraulic fluid back into the tank through the drain valve
, The measuring circuit is suitable for reciprocating load occasions such as
machine tools and other load fluctuations due to back pressure on the oil return
side. The efficiency of
this loop is not high at about 30% .
9-3-3 bleeder (Bleed-off) circuit P521 TOP
The flow control valve is placed on the branch on the inlet side of the hydraulic cylinder, and excess hydraulic oil flows back to the oil tank through the flow control valve. The circuit pressure is directly determined by the working pressure of the hydraulic cylinder, so there is less heat loss and higher efficiency. The bleeder circuit is used when the load fluctuation is small. The loop efficiency is the highest of the three.
9-3-4 deceleration circuit (with Deceleration Circuit) P521 the TOP
9-3-5 Differential Circuit (Differential Circuit) P522 TOP
9-3-6 hydraulic oil supplement circuit (prefill Circuit) P523 TOP
9-3-7 Synchronizing Circuit (Synchronizing Circuit) P526
( 2 ) Synchronous circuit of diverter valve P527 TOP
( 3 ) Synchronous circuit TOP of hydraulic cylinders connected in series
( 4 ) Synchronous circuit P528 TOP of independent hydraulic pump
( 5 ) Synchronous circuit of independent hydraulic motor P529 TOP
( 6 ) Synchronous circuit P529 TOP that mechanically connects two hydraulic cylinders
9-3-8 P530 TOP combined pneumatic and hydraulic circuit
9-4 Hydraulic motor control circuit P531 TOP
9-4-2 series with the circuit P531 TOP
9-4-2 parallel circuit P532 TOP
9-4- 3 Constant torque circuit Figure 9-62 TOP
9-4-4 fix power circuit Figure 9-63 P533 TOP
9-4-5 hydraulic motor counterbalance circuit P534 TOP
9-4-6 Brake circuit P535 TOP
9-5 Electrical - hydraulic
control circuit P536 TOP 9-5-1 Electrical - directional
control circuit
9-5-2 measuring circuit P538 TOP
9-5-3 measuring circuit P539 TOP
9-5-4 differential back path P5 41 is the TOP
9-5-5 Two-stage speed change circuit P5 42 TOP
9-5-6 synchronous circuit of hydraulic cylinders in parallel P5 43 TOP
9-5-7 Synchronous circuit of hydraulic cylinders in series P545 TOP
9-5-8 Pressure reducing circuit P546 TOP
9-5-9 pressure holding circuit P5 48 TOP
9-5-10 counterbalance circuit P5 49 TOP
9-5-11 Sequence circuit P5 50 TOP
9-5-12 Accumulator circuit P5 52 TOP
9-5-13 Pressure switch circuit P5 53 TOP
9-5-14 hydraulic motor circuit P5 54 TOP
Goto Zulie teacher teaching network gas hydraulic control practice